Getting Started with Katib
This guide shows how to get started with Katib and run a few examples using the command line and the Katib user interface (UI) to perform hyperparameter tuning.
For an overview of the concepts around Katib and hyperparameter tuning, check the introduction to Katib.
Katib setup
Let’s set up and configure Katib on your Kubernetes cluster with Kubeflow.
Prerequisites
This is the minimal requirements to install Katib:
- Kubernetes >= 1.27
kubectl>= 1.27
Installing Katib
You can skip this step if you have already installed Kubeflow. Your Kubeflow deployment includes Katib.
To install Katib as part of Kubeflow, follow the Kubeflow installation guide.
If you want to install Katib separately from Kubeflow, or to get a later version
of Katib, you can use one of the following Katib installs. To install the specific
Katib release (e.g. v0.11.1), modify ref=master to ref=v0.11.1.
Katib Standalone Installation
There are two ways to install Katib by standalone, both of which do not require any additional setup on your Kubernetes cluster.
Basic Installation
Run the following command to deploy the default Katib Control Plane components: (
katib-controller,katib-ui,katib-mysql, andkatib-db-manager):kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-standalone?ref=master"Controller Leader Election Support
Run the following command to deploy Katib with Controller Leader Election:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-leader-election?ref=master"This installation is almost the same as
Basic Installation, although you can makekatib-controllerHighly Available (HA) using leader election. If you plan to use Katib in an environment where high Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and Service Level Objectives (SLOs) are required, such as a production environment, consider choosing this installation.
Katib Cert Manager Installation
Run the following command to deploy Katib with Cert Manager requirement:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-cert-manager?ref=master"This installation uses Cert Manager instead of Katib certificate generator to provision Katib webhooks certificates. You have to deploy Cert Manager on your Kubernetes cluster before deploying Katib using this installation.
Katib External DB Installation
Run the following command to deploy Katib with custom Database (DB) backend:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-external-db?ref=master"This installation allows to use custom MySQL DB instead of
katib-mysql. You have to modify appropriate environment variables forkatib-db-managerin thesecrets.envto point at your custom MySQL DB. Learn more aboutkatib-db-managerenvironment variables in this guide.Katib on OpenShift
Run the following command to deploy Katib on OpenShift v4.4+:
kubectl apply -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-openshift?ref=master"This installation uses OpenShift service controller instead of Katib certificate generator to provision Katib webhooks certificates.
Above installations deploy PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) for the Katib DB component.
Your Kubernetes cluster must have StorageClass for dynamic volume provisioning.
For more information, check the Kubernetes documentation on
dynamic provisioning.
If your cluster doesn’t have dynamic volume provisioning, you must manually deploy PersistentVolume (PV) to bind PVC for the Katib DB component.
Katib components
Run the following command to verify that Katib components are running:
$ kubectl get pods -n kubeflow
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
katib-controller-566595bdd8-8w7sx 1/1 Running 0 82s
katib-db-manager-57cd769cdb-vt7zs 1/1 Running 0 82s
katib-mysql-7894994f88-djp7m 1/1 Running 0 81s
katib-ui-5767cfccdc-v9fcs 1/1 Running 0 80s
katib-controller- the controller to manage Katib Kubernetes CRDs (Experiment,Suggestion,Trial).- (Optional) If certificate generator is enabled in Katib Config, Katib controller deployment will create self-signed certificate for the Katib webhooks. Learn more about the cert generator in the developer guide.
katib-ui- the Katib user interface.katib-db-manager- the GRPC API server to control Katib DB interface.katib-mysql- themysqlDB backend to store Katib experiments metrics.
Accessing the Katib UI
You can use the Katib user interface (UI) to submit experiments and to monitor your results. The Katib home page within Kubeflow looks like this:
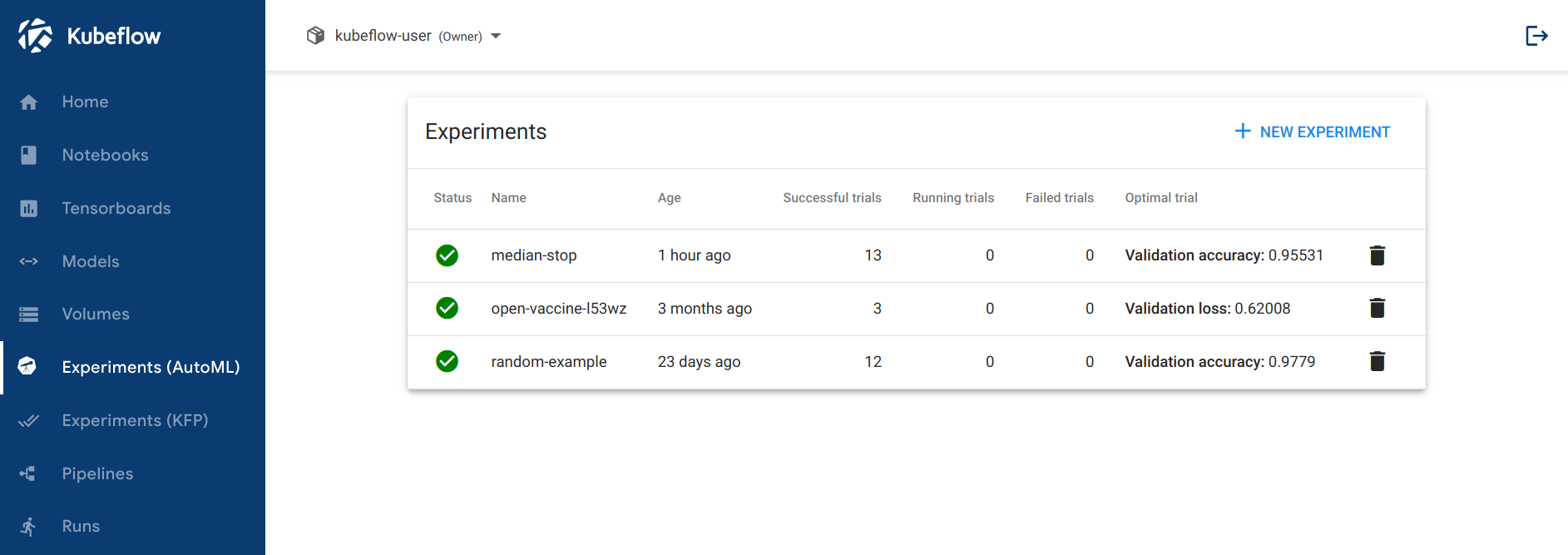
If you installed Katib as part of Kubeflow, you can access the Katib UI from the Kubeflow UI:
- Open the Kubeflow UI. Check the guide to accessing the central dashboard.
- Click Katib in the left-hand menu.
Alternatively, you can set port-forwarding for the Katib UI service:
kubectl port-forward svc/katib-ui -n kubeflow 8080:80
Then you can access the Katib UI at this URL:
http://localhost:8080/katib/
Check this guide if you want to contribute to Katib UI.
Examples
This section introduces some examples that you can run to try Katib.
Quickstart with Katib SDK
You can run your first HyperParameter Tuning Experiment using Katib Python SDK.
In the following example we are going to maximize a simple objective function:
$F(a,b) = 4a - b^2$
The bigger $a$ and the lesser $b$ value, the bigger the function value $F$.
import kubeflow.katib as katib
# Step 1. Create an objective function.
def objective(parameters):
# Import required packages.
import time
time.sleep(5)
# Calculate objective function.
result = 4 * int(parameters["a"]) - float(parameters["b"]) ** 2
# Katib parses metrics in this format: <metric-name>=<metric-value>.
print(f"result={result}")
# Step 2. Create HyperParameter search space.
parameters = {
"a": katib.search.int(min=10, max=20),
"b": katib.search.double(min=0.1, max=0.2)
}
# Step 3. Create Katib Experiment with 12 Trials and 2 GPUs per Trial.
katib_client = katib.KatibClient()
name = "tune-experiment"
katib_client.tune(
name=name,
objective=objective,
parameters=parameters,
objective_metric_name="result",
max_trial_count=12,
resources_per_trial={"gpu": "2"},
)
# Step 4. Get the best HyperParameters.
print(katib_client.get_optimal_hyperparameters(name))
Example using random search algorithm
You can create an experiment for Katib by defining the experiment in a YAML configuration file. The YAML file defines the configurations for the experiment, including the hyperparameter feasible space, optimization parameter, optimization goal, suggestion algorithm, and so on.
This example uses the YAML file for the random search example.
The random search algorithm example uses an MXNet neural network to train an image classification model using the MNIST dataset. You can check training container source code here. The experiment runs twelve training jobs with various hyperparameters and saves the results.
If you installed Katib as part of Kubeflow, you can’t run experiments in the Kubeflow namespace. Run the following commands to change namespace and launch an experiment using the random search example:
Download the example:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeflow/katib/master/examples/v1beta1/hp-tuning/random.yaml --output random.yamlEdit
random.yamland change the following line to use your Kubeflow user profile namespace (e.g.kubeflow-user-example-com):namespace: kubeflow(Optional) Note: Katib’s experiments don’t work with Istio sidecar injection. If you are using Kubeflow with Istio, you have to disable sidecar injection. To do that, specify this annotation:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"in your experiment’s trial template.For the provided random search example with Kubernetes
Jobtrial template, annotation should be under.trialSpec.spec.template.metadata.annotations. For the KubeflowTFJobor other training operators check here how to set the annotation.Deploy the example:
kubectl apply -f random.yaml
This example embeds the hyperparameters as arguments. You can embed
hyperparameters in another way (for example, using environment variables)
by using the template defined in the trialTemplate.trialSpec section of
the YAML file. The template uses the
unstructured
format and substitutes parameters from the trialTemplate.trialParameters.
Follow the trial template guide
to know more about it.
This example randomly generates the following hyperparameters:
--lr: Learning rate. Type: double.--num-layers: Number of layers in the neural network. Type: integer.--optimizer: Optimization method to change the neural network attributes. Type: categorical.
Check the experiment status:
kubectl -n kubeflow-user-example-com get experiment random -o yaml
The output of the above command should look similar to this:
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1beta1
kind: Experiment
metadata:
...
name: random
namespace: kubeflow-user-example-com
...
spec:
algorithm:
algorithmName: random
maxFailedTrialCount: 3
maxTrialCount: 12
metricsCollectorSpec:
collector:
kind: StdOut
objective:
additionalMetricNames:
- Train-accuracy
goal: 0.99
metricStrategies:
- name: Validation-accuracy
value: max
- name: Train-accuracy
value: max
objectiveMetricName: Validation-accuracy
type: maximize
parallelTrialCount: 3
parameters:
- feasibleSpace:
max: "0.03"
min: "0.01"
name: lr
parameterType: double
- feasibleSpace:
max: "5"
min: "2"
name: num-layers
parameterType: int
- feasibleSpace:
list:
- sgd
- adam
- ftrl
name: optimizer
parameterType: categorical
resumePolicy: Never
trialTemplate:
failureCondition: status.conditions.#(type=="Failed")#|#(status=="True")#
primaryContainerName: training-container
successCondition: status.conditions.#(type=="Complete")#|#(status=="True")#
trialParameters:
- description: Learning rate for the training model
name: learningRate
reference: lr
- description: Number of training model layers
name: numberLayers
reference: num-layers
- description: Training model optimizer (sdg, adam or ftrl)
name: optimizer
reference: optimizer
trialSpec:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"
spec:
containers:
- command:
- python3
- /opt/mxnet-mnist/mnist.py
- --batch-size=64
- --lr=${trialParameters.learningRate}
- --num-layers=${trialParameters.numberLayers}
- --optimizer=${trialParameters.optimizer}
image: docker.io/kubeflowkatib/mxnet-mnist:v1beta1-45c5727
name: training-container
restartPolicy: Never
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-10-07T21:12:06Z"
lastUpdateTime: "2021-10-07T21:12:06Z"
message: Experiment is created
reason: ExperimentCreated
status: "True"
type: Created
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-10-07T21:12:28Z"
lastUpdateTime: "2021-10-07T21:12:28Z"
message: Experiment is running
reason: ExperimentRunning
status: "True"
type: Running
currentOptimalTrial:
bestTrialName: random-hpsrsdqp
observation:
metrics:
- latest: "0.993054"
max: "0.993054"
min: "0.917694"
name: Train-accuracy
- latest: "0.979598"
max: "0.979598"
min: "0.957106"
name: Validation-accuracy
parameterAssignments:
- name: lr
value: "0.024736875661534784"
- name: num-layers
value: "4"
- name: optimizer
value: sgd
runningTrialList:
- random-2dwxbwcg
- random-6jd8hmnd
- random-7gks8bmf
startTime: "2021-10-07T21:12:06Z"
succeededTrialList:
- random-xhpcrt2p
- random-hpsrsdqp
- random-kddxqqg9
- random-4lkr5cjp
trials: 7
trialsRunning: 3
trialsSucceeded: 4
When the last value in status.conditions.type is Succeeded, the experiment
is complete. You can check information about the best trial in status.currentOptimalTrial.
.currentOptimalTrial.bestTrialNameis the trial name..currentOptimalTrial.observation.metricsis themax,minandlatestrecorded values for objective and additional metrics..currentOptimalTrial.parameterAssignmentsis the corresponding hyperparameter set.
In addition, status shows the experiment’s trials with their current status.
View the results of the experiment in the Katib UI:
Open the Katib UI as described above.
You should be able to view the list of experiments:
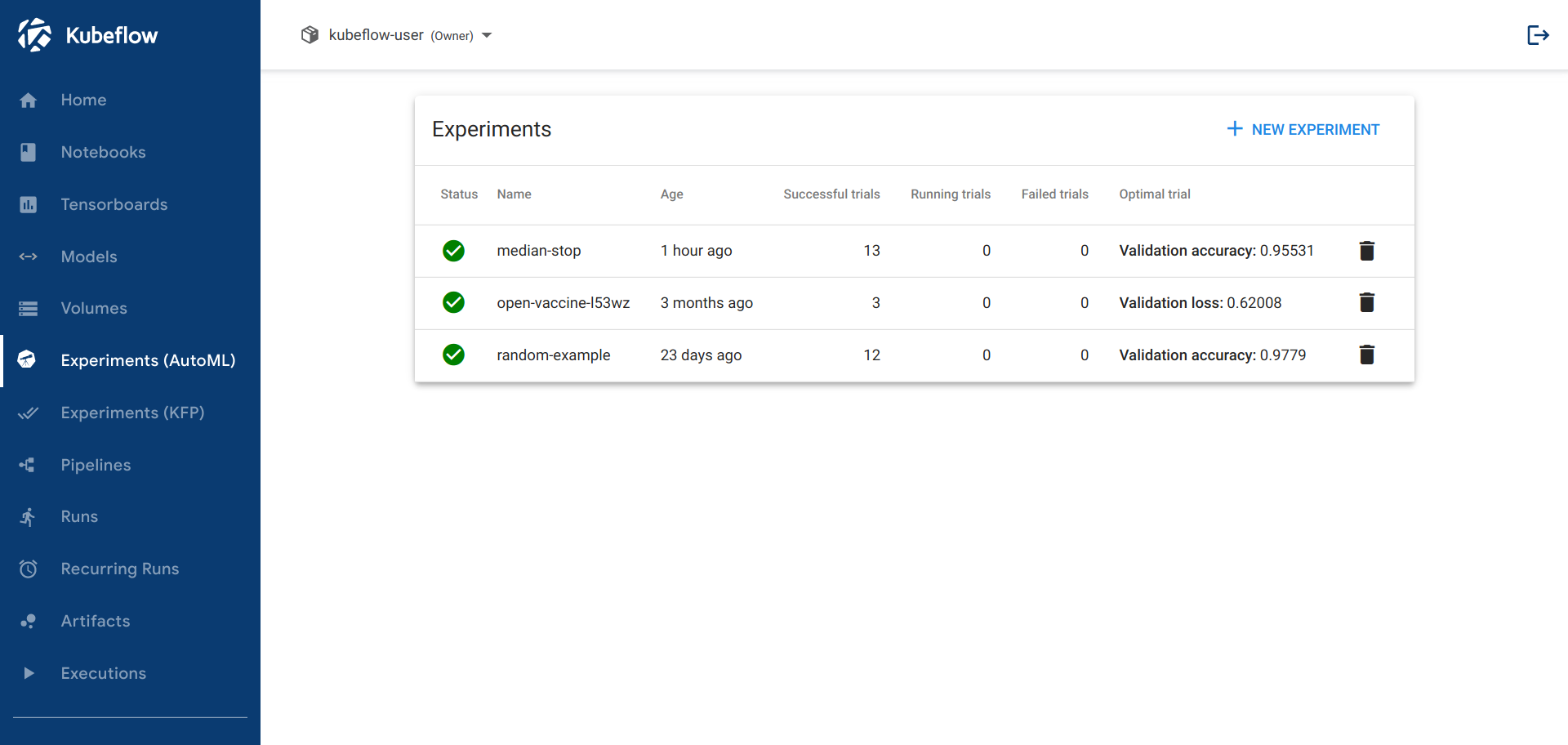
Click the name of the experiment, random-example.
There should be a graph showing the level of validation and train accuracy for various combinations of the hyperparameter values (learning rate, number of layers, and optimizer):
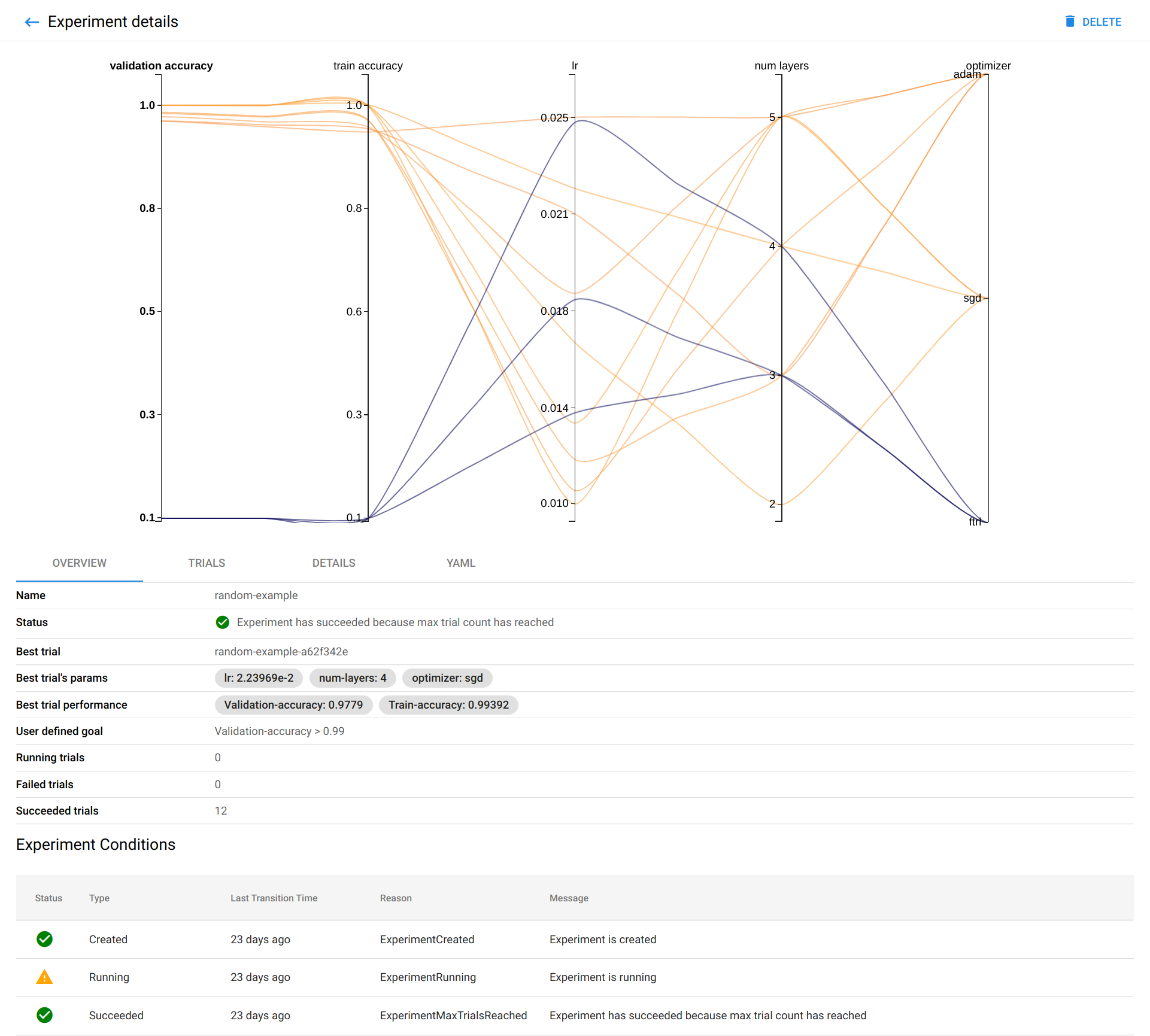
Below the graph is a list of trials that ran within the experiment:
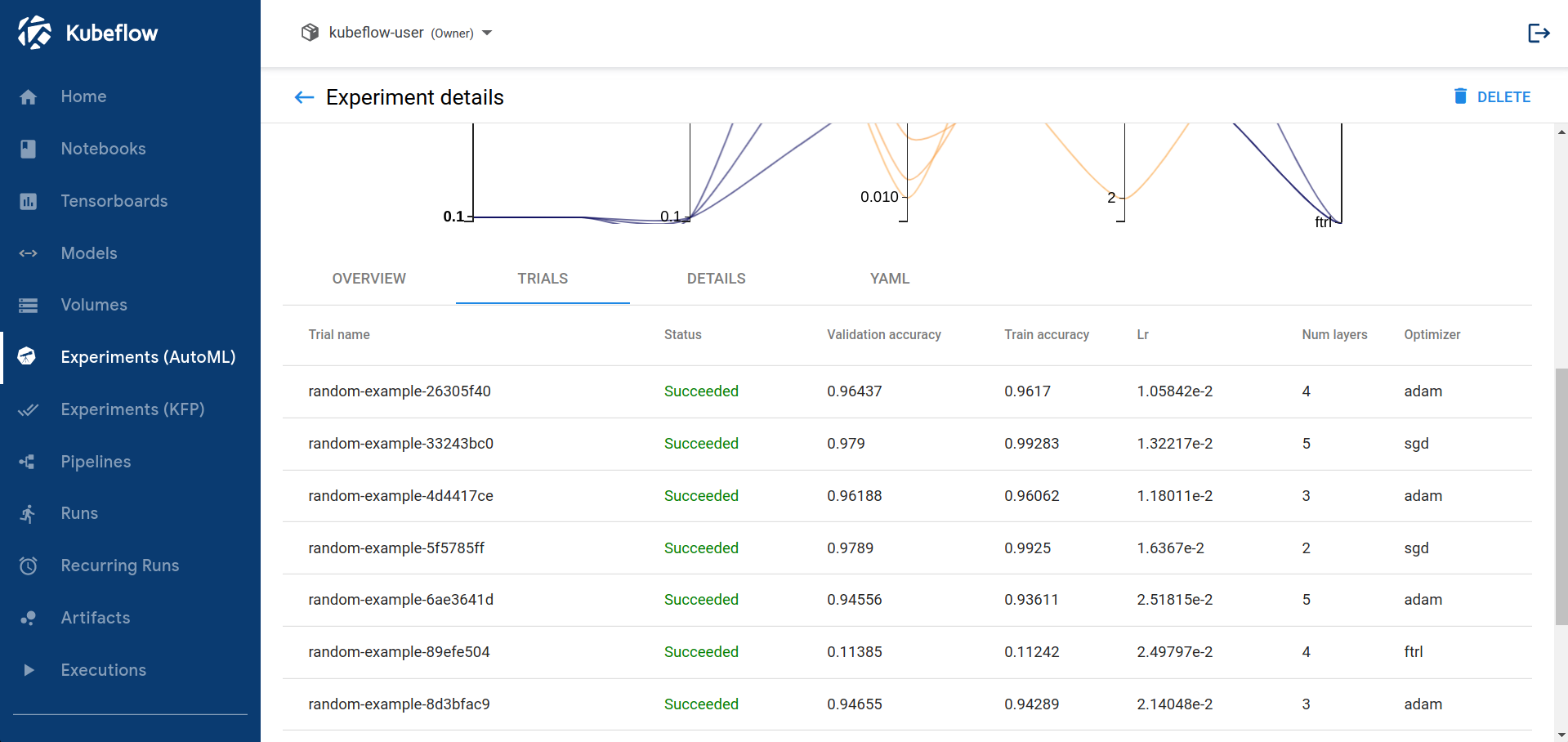
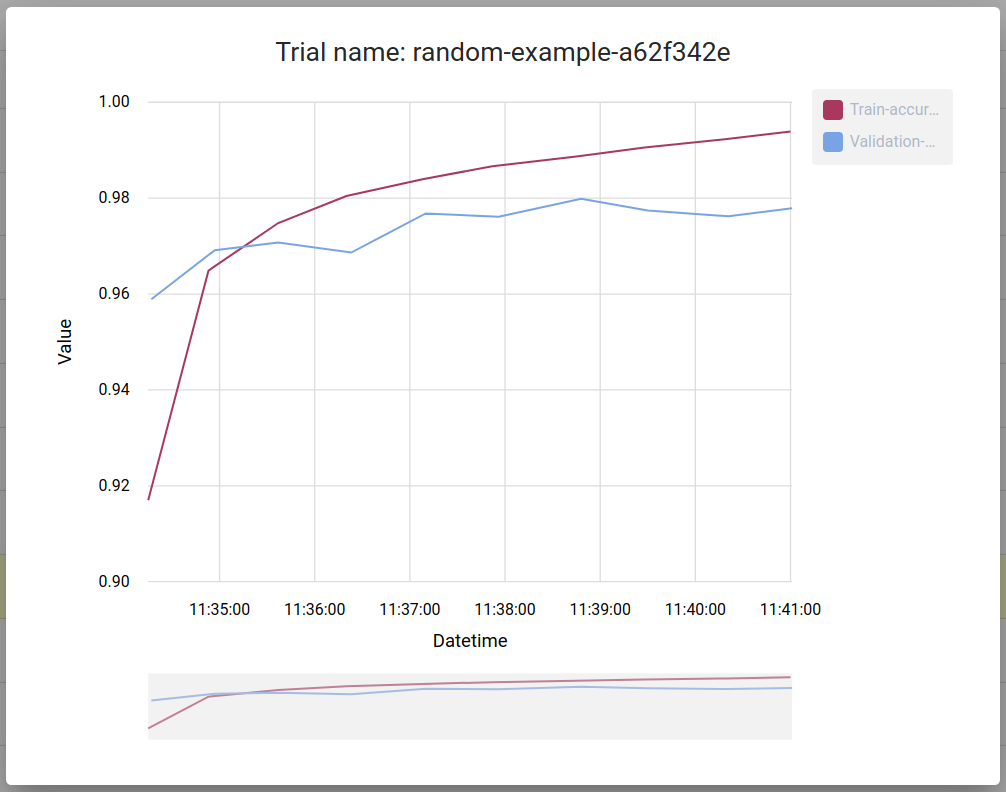
You can click on trial name to get metrics for the particular trial:
TensorFlow example
If you installed Katib as part of Kubeflow, you can’t run experiments in the
Kubeflow namespace. Run the following commands to launch an experiment using
the Kubeflow’s TensorFlow training job operator, TFJob:
Download
tfjob-mnist-with-summaries.yaml:curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeflow/katib/master/examples/v1beta1/kubeflow-training-operator/tfjob-mnist-with-summaries.yaml --output tfjob-mnist-with-summaries.yamlEdit
tfjob-mnist-with-summaries.yamland change the following line to use your Kubeflow user profile namespace (e.g.kubeflow-user-example-com):namespace: kubeflow(Optional) Note: Katib’s experiments don’t work with Istio sidecar injection. If you are using Kubeflow with Istio, you have to disable sidecar injection. To do that, specify this annotation:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"in your experiment’s trial template. For the providedTFJobexample check here how to set the annotation.Deploy the example:
kubectl apply -f tfjob-mnist-with-summaries.yamlYou can check the status of the experiment:
kubectl -n kubeflow-user-example-com get experiment tfjob-mnist-with-summaries -o yaml
Follow the steps as described for the random search algorithm example above to obtain the results of the experiment in the Katib UI.
PyTorch example
If you installed Katib as part of Kubeflow, you can’t run experiments in the
Kubeflow namespace. Run the following commands to launch an experiment
using Kubeflow’s PyTorch training job operator, PyTorchJob:
Download
pytorchjob-mnist.yaml:curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeflow/katib/master/examples/v1beta1/kubeflow-training-operator/pytorchjob-mnist.yaml --output pytorchjob-mnist.yamlEdit
pytorchjob-mnist.yamland change the following line to use your Kubeflow user profile namespace (e.g.kubeflow-user-example-com):namespace: kubeflow(Optional) Note: Katib’s experiments don’t work with Istio sidecar injection. If you are using Kubeflow with Istio, you have to disable sidecar injection. To do that, specify this annotation:
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"in your experiment’s trial template. For the providedPyTorchJobexample setting the annotation should be similar toTFJobDeploy the example:
kubectl apply -f pytorchjob-mnist.yamlYou can check the status of the experiment:
kubectl -n kubeflow-user-example-com describe experiment pytorchjob-mnist
Follow the steps as described for the random search algorithm example above to get the results of the experiment in the Katib UI.
Cleaning up
To remove Katib from your Kubernetes cluster run:
kubectl delete -k "github.com/kubeflow/katib.git/manifests/v1beta1/installs/katib-standalone?ref=master"
Next steps
Learn how to configure and run your Katib experiments.
Learn to configure your trial templates.
Check the Katib Configuration (Katib config).
How to set up environment variables for each Katib component.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.